Introduction :
In Modern Fortran , program is separated to a structure that have a main file and connect with multi-library , that have Module structure. This new feature is so powerful and improve development standard better before.
In this picture , Main program is using 3 library module called : Module_1, Module_2, Module_3 , and only Module_1 and Module_2 is need to import directly to Main program . The green arrow mean “import” or “USE syntax” in this picture.
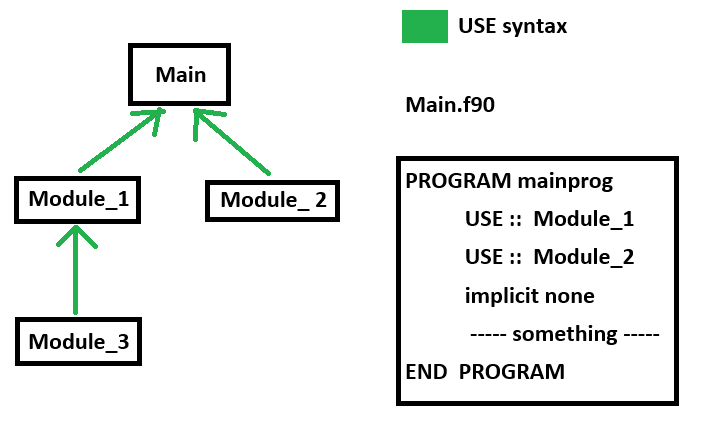
How Module Structure look like !
Under code block , the module name is written after MODULE syntax and END MODULE syntax , and called “stla_io” in this example . Later, this module name can be used to import to main file or other module file using USE syntax.
MODULE stla_io
----------------------- something ------------
END MODULE stla_ioNext to module name , we will have space for define some new feature of modern fortran :
USEsyntax : import external library or other module to use some external function
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
----------------------- something ------------
END MODULE stla_io- PARAMETER , SAVE variables : we will need this sometime for mathematic
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
INTEGER, PARAMETER :: some_parameter
INTEGER, SAVE :: some_save_variable
------ PARAMETER or SAVE variables -----
----------------------- something ------------
END MODULE stla_ioTYPEsyntax : of course , Modern Fortran is object-oriented languages , define some object like monster or player for your 2d games here
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
------ PARAMETER or SAVE variables -----
TYPE :: Object_type
---- OBJECT DEFINE ----
END TYPE Object_type
----------------------- something ------------
END MODULE stla_io- INTERFACE syntax : it have 2 purpose, one is for create a interface for other language functions like as C\C++ , winapi . We only need C library header file for compile process, and setup linker for these library later when compile with main file in last process . Second is for define generic name for functions that have multi-version. In general , all multi-version functions need be place after CONTAINS syntax in module file.
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
------ PARAMETER or SAVE variables -----
------- OBJECT DEFINE ----------
INTEFACE
--- EXTERNAL C/C++ FUNCTION INTERFACE----
END INTERFACE
INTEFACE generic_name
--- GENERIC SUBROUTINE ----
END INTERFACE
----------------------- something ------------
END MODULE stla_io- CONTAINS syntax : the traditional subroutines and functions define will be place after breakline of this syntax . We can use INCLUDE syntax to import all old library file to this CONTAINS block, but rewrite to new standard may be better.
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
------ PARAMETER or SAVE variables -----
------- OBJECT DEFINE ----------
------- EXTERNAL C/C++ FUNCTION INTERFACE ----
------- GENERIC SUBROUTINE INTERFACE ----
CONTAINS
-------- SUBROUTINE, FUNCTION DIFINE ------------
END MODULE stla_ioAfter all, combine all upper things , we have module file look like under code :
MODULE stla_io
USE :: somelib , only : somefunction
implicit none
INTEGER, PARAMETER :: some_parameter
INTEGER, SAVE :: some_save_variable
------ PARAMETER or SAVE variables -----
TYPE :: Object_type
---- OBJECT DEFINE ----
END TYPE Object_type
INTEFACE
--- EXTERNAL C/C++ FUNCTION INTERFACE----
END INTERFACE
INTEFACE generic_name
--- GENERIC SUBROUTINE ----
END INTERFACE
CONTAINS
------- old-fortran-lib-if-want-to-include ---
INCLUDE ".\old_subroutine_fortran_file.f90"
subroutine subroutine_of_this_module
------- subroutine define ----
end subroutine
END MODULE stla_io
Leave a Reply